The Nation’s Fiscal Health: Federal Action Critical to Pivot toward Fiscal Sustainability
GAO-22-105376 Published: May 05, 2022. Publicly Released: May 05, 2022 – Excerpts:
The federal government faces an unsustainable fiscal future. If policies don’t change, debt will continue to grow faster than the economy. This year’s review of the nation’s fiscal health found:
- Large annual budget deficits drive debt growth, as the government borrows money to finance spending that exceeds revenue
- Medicare and Social Security costs drive spending increases, especially as the population continues to get older
- Interest costs are projected to grow and could increase even faster if interest rates rise more than expected
Difficult policy decisions are needed to address the growing debt and change the government’s fiscal path.
What GAO Found
The federal government faces an unsustainable fiscal future. At the end of fiscal year 2021, debt held by the public was about 100 percent of gross domestic product (GDP), a 33 percent increase from fiscal year 2019. Projections from the Office of Management and Budget and the Department of the Treasury, the Congressional Budget Office, and GAO all show that current fiscal policy is unsustainable over the long term. Debt held by the public is projected to reach its historical high of 106 percent of GDP within 10 years and continue to grow at an increasing pace. This ratio could reach 217 percent of GDP by 2050, absent any change in fiscal policy.
Debt Held by the Public Projected to Grow Faster Than GDP
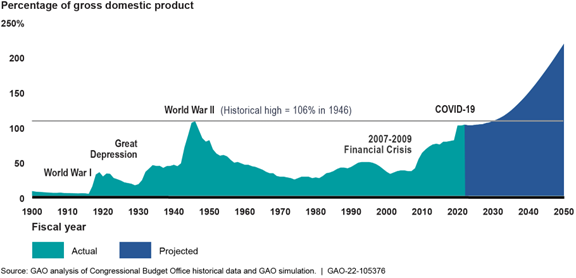
The underlying conditions driving this unsustainable fiscal outlook existed well before the COVID-19 pandemic and continue to pose serious challenges if not addressed.
Federal Budget Deficit in Fiscal Year 2021 was Second Largest in History
The fiscal year 2021 federal budget deficit of $2.8 trillion was the second largest in history, after the fiscal year 2020 deficit of $3.1 trillion. These historically large deficits were due primarily to economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic—which decreased revenues in fiscal year 2020—and the additional spending by the federal government in response to the pandemic. Federal debt held by the public grew by about $5.5 trillion during fiscal years 2020 and 2021, reaching $22.3 trillion at the end of fiscal year 2021.
Increasingly Large Deficits Drive Unsustainable Debt Levels
In GAO’s simulation, starting in 2024, debt held by the public grows faster than GDP in every year. In most years, debt held by the public grows more than twice as fast as the economy, in real terms. The growing debt is a consequence of borrowing to finance increasingly large annual budget deficits. The total budget deficit is composed of two parts:
- The primary deficit: the gap between non-interest (program) spending and revenue and
- Spending on net interest: primarily the cost to service the debt.
Primary Deficit and Total Budget Deficit, Actual and Projected
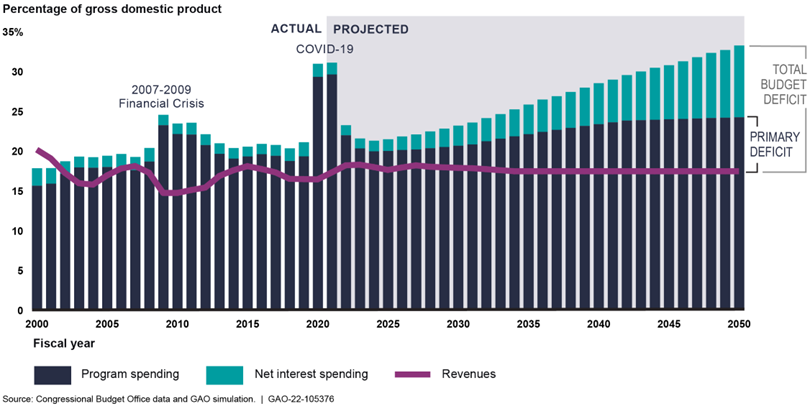
In GAO’s simulation, increasing primary deficits are driving spending and revenue trends.
- Spending: Medicare, other federal health care programs, and Social Security are requiring an increasingly large share of federal resources. Under GAO’s simulation, spending for both major federal health care programs and Social Security would account for 85 percent of projected revenue in 2050, up from 63 percent in 2019.
- Revenue: Average annual revenue as a share of GDP was lower over the last 20 years than in prior decades. From 2000 to 2021, revenue averaged 16.8 percent of GDP annually, compared to annual average of 17.9 percent of GDP between 1980 and 2000.
______________________________________
Note – There is ‘no political will’ among either Washington Democrats or Washington Republicans to effect any meaningful changes to address the GAO’s dire fiscal forecast for the U.S..
Their non-action is both shameful and dangerous.
Main Street Republicans, however, do have a plan – one that re-targets Federal Reserve monetary policy to create enormous fiscal benefits and long-term financial viability for the United States.
This Plan will generate $583 billion budget surpluses, conservatively, each of the first five years of activation (2023-2027); reduce / eliminate America’s $3.2 trillion in state and local debt; and provided for a massive reduction in the $16.15 trillion of Household Debt carried by America’s families.
The Leviticus 25 Plan is a dynamic economic initiative providing direct liquidity benefits for American families, while at the same time scaling back the role of government in managing and controlling the affairs of citizens. It is a comprehensive plan with long-term economic and social benefits for citizens and government.
The inspiration for this plan is based upon Biblical principles set forth in the Book of Leviticus, principles tendering direct economic liberties to the people.
The Leviticus 25 Plan – An Economic Acceleration Plan for America
$90,000 per U.S. citizen – Leviticus 25 Plan 2023 (4174 downloads)
